The GWAS Catalog provides a consistent, searchable, visualisable and freely available database of SNP-trait associations, which can be easily integrated with other resources.
The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) Portal provides open access to data including gene expression, QTLs, and histology static.
The Human Genome Browser includes a broad collection of vertebrate and model organism assemblies and annotations, along with a large suite of tools for viewing, analyzing and downloading data.
BRAVO variant browser shows chromosome locations (on GRCh38 human genome assembly), alleles, functional annotations, and allele frequencies for 705 million variants observed in 132,345 deeply sequenced (>38X) genomes from the TOPMed (Trans-Omics for Precision Medicine) data freeze 8.

LitVar allows the search and retrieval of variant relevant information from the biomedical literature and shows key biological relations between a variant and its close related entities (e.g. genes, diseases, and drugs).
The OpenTargets Genetics Portal is a tool highlighting variant-centric statistical evidence to allow both prioritisation of candidate causal variants at trait-associated loci and identification of potential drug targets.
The European Variation Archive is an open-access database of all types of genetic variation data from all species.

PheWeb is an easy-to-use open-source web-based tool for visualizing, navigating, and sharing GWAS and PheWAS results.
dbSNP contains human single nucleotide variations, microsatellites, and small-scale insertions and deletions along with publication, population frequency, molecular consequence, and genomic and RefSeq mapping information for both common variations and clinical mutations.
DisGeNET is a discovery platform containing one of the largest publicly available collections of genes and variants associated to human diseases.
The Genome Aggregation Database (gnomAD) is a resource developed by an international coalition of investigators, with the goal of aggregating and harmonizing both exome and genome sequencing data from a wide variety of large-scale sequencing projects, and making summary data available for the wider scientific community.
GWAS Central provides a centralized compilation of summary level findings from genetic association studies, both large and small.
PharmGKB is a comprehensive resource that curates knowledge about the impact of genetic variation on drug response for clinicians and researchers.
SNPedia is a wiki investigating human genetics. It shares information about the effects of variations in DNA, citing peer-reviewed scientific publications.
SpliceAI is a deep neural network that accurately predicts splice junctions from an arbitrary pre-mRNA transcript sequence, enabling precise prediction of noncoding genetic variants that cause cryptic splicing.
CADD is a tool for scoring the deleteriousness of single nucleotide variants as well as insertion/deletions variants in the human genome.
ClinVar aggregates information about genomic variation and its relationship to human health.
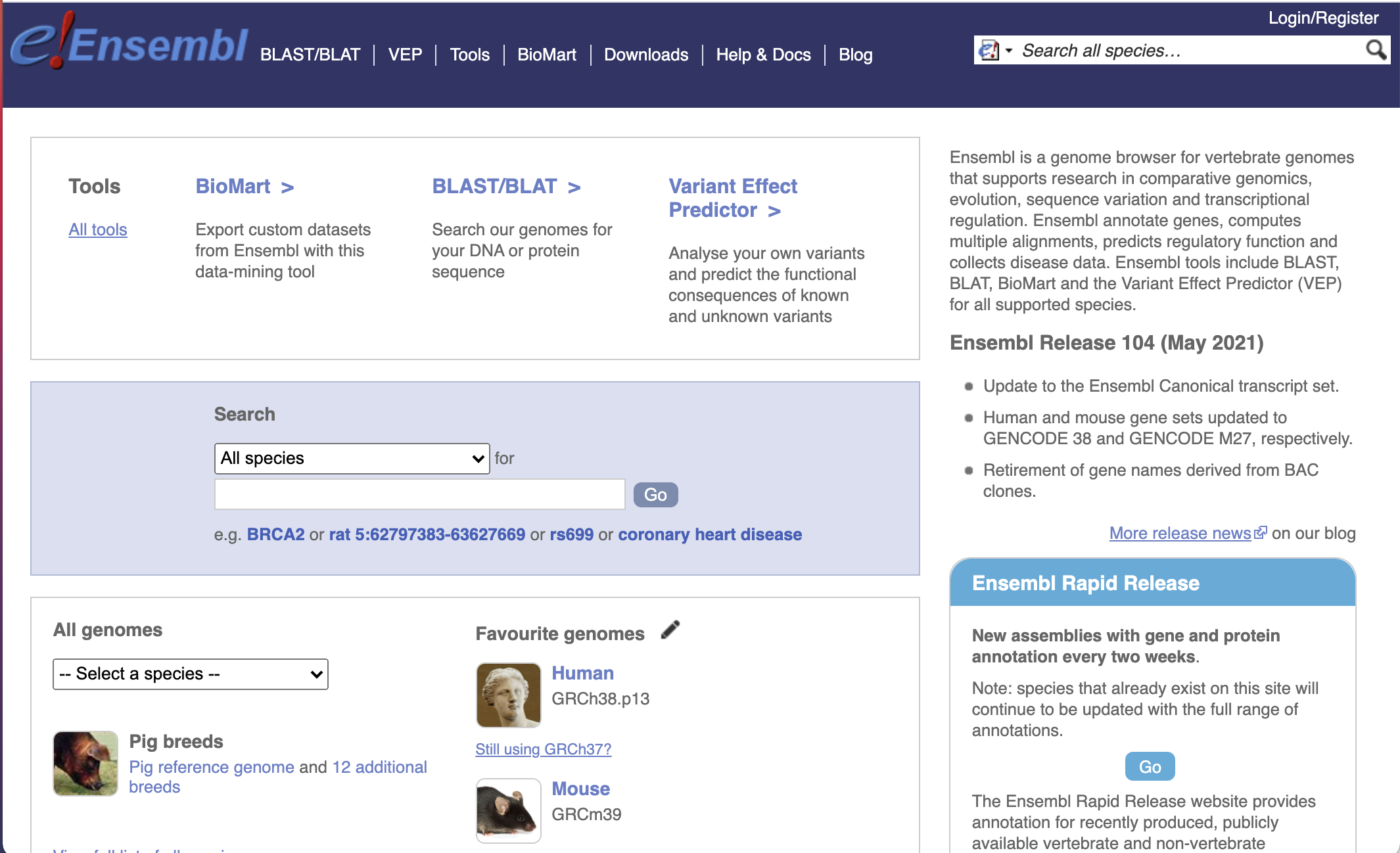
Ensembl is a genome browser for vertebrate genomes that supports research in comparative genomics, evolution, sequence variation and transcriptional regulation.