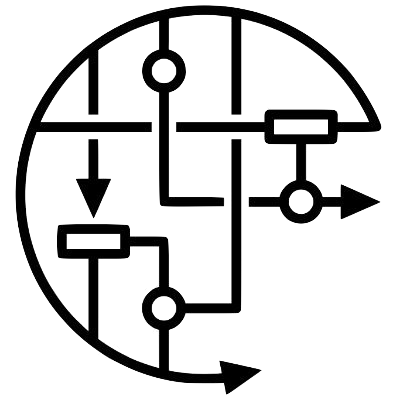
Gene and Drug Landing Page Aggregator
Gene and Drug Landing Page Aggregator (GDLPA) has links to 53 gene, 18 variant and 19 drug repositories that provide direct links to gene and drug landing pages. You can search by gene or drug name and then choose the sites that contain knowledge about your gene or drug of interest. Resources supported by the NIH Common Fund are listed first and have the CFDE logo at their top right corner.
The GWAS Catalog provides a consistent, searchable, visualisable and freely available database of SNP-trait associations, which can be easily integrated with other resources.
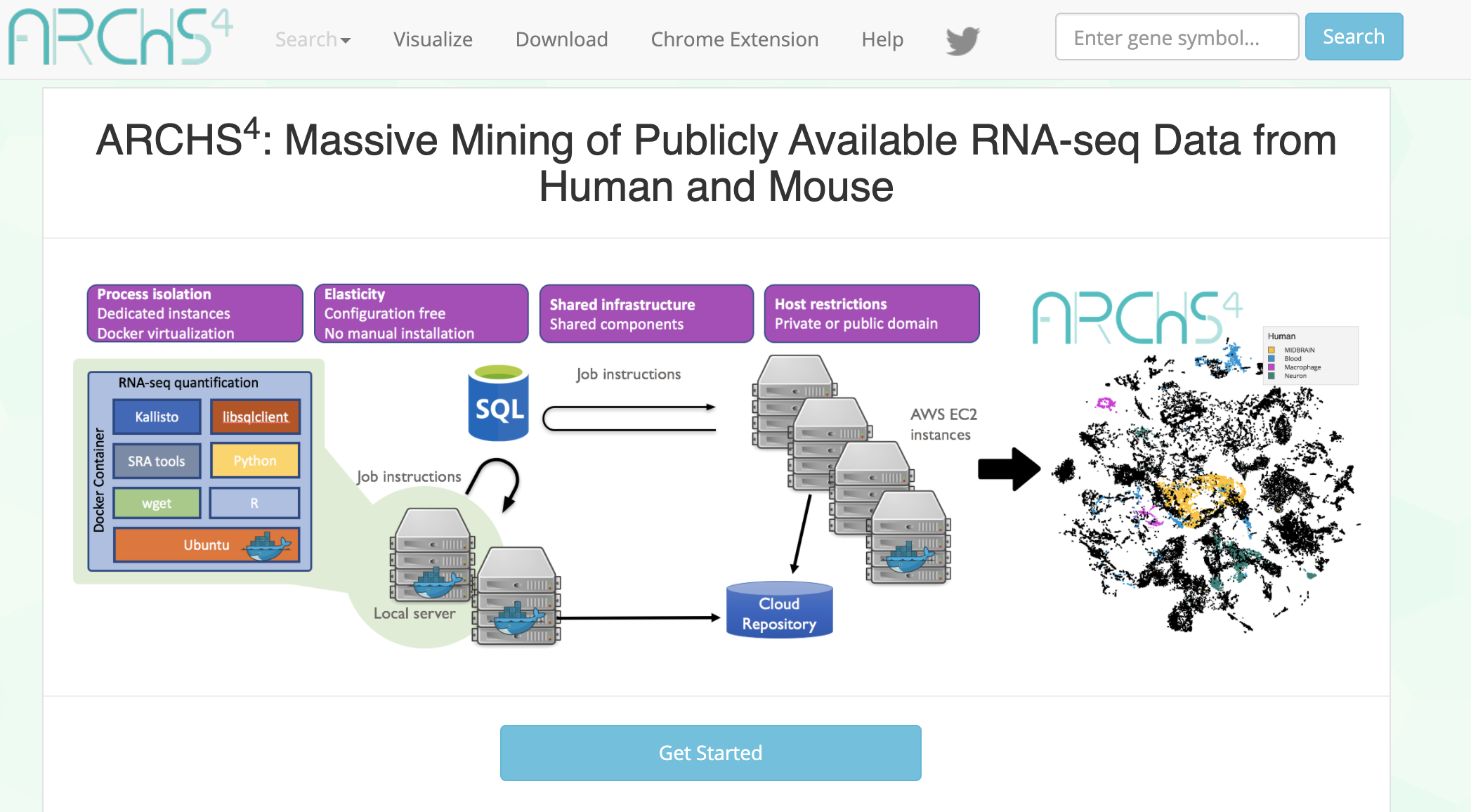
ARCHS4 provides access to gene counts from HiSeq 2000, HiSeq 2500 and NextSeq 500 platforms for human and mouse experiments from GEO and SRA.
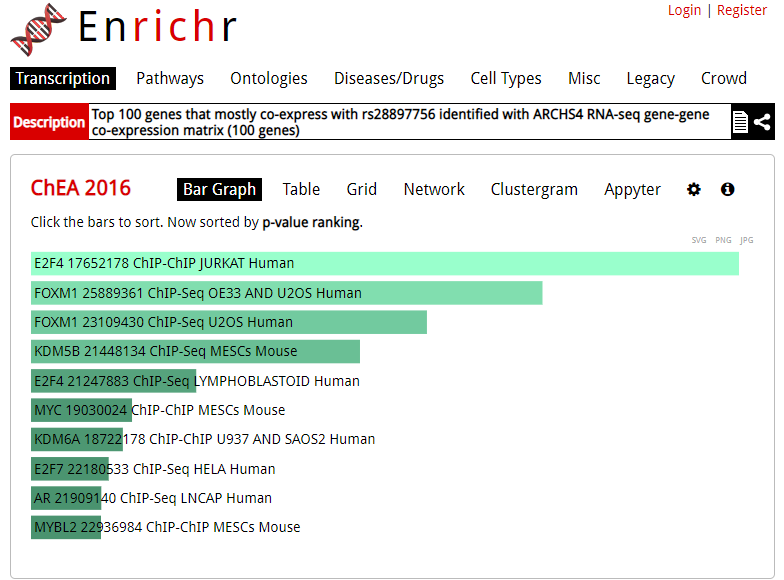
Enrichr is an enrichment analysis tool that provides various types of visualization summaries of collective functions of gene sets.
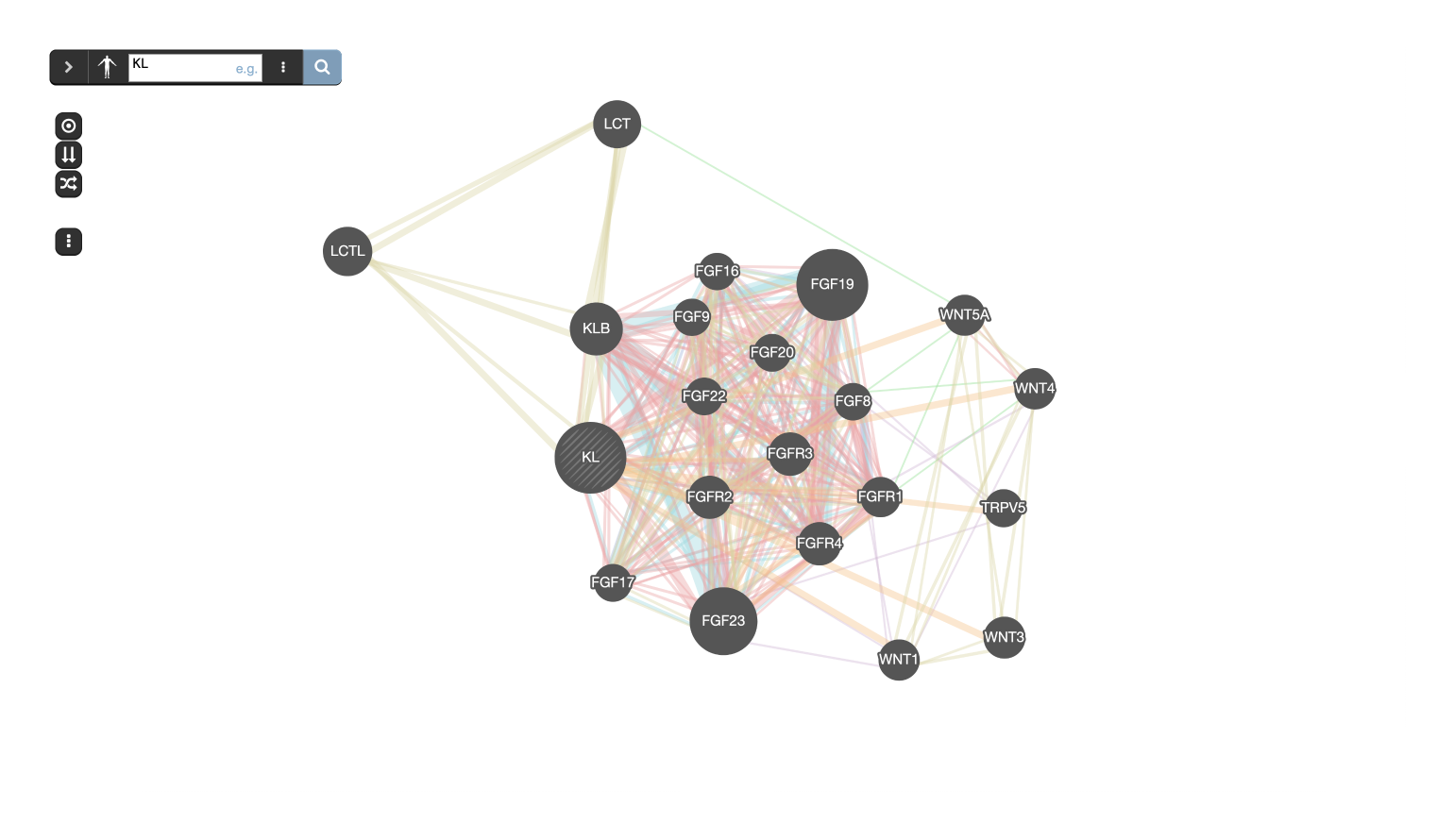
GeneMANIA builds subnetworks around an input gene using functional association data.
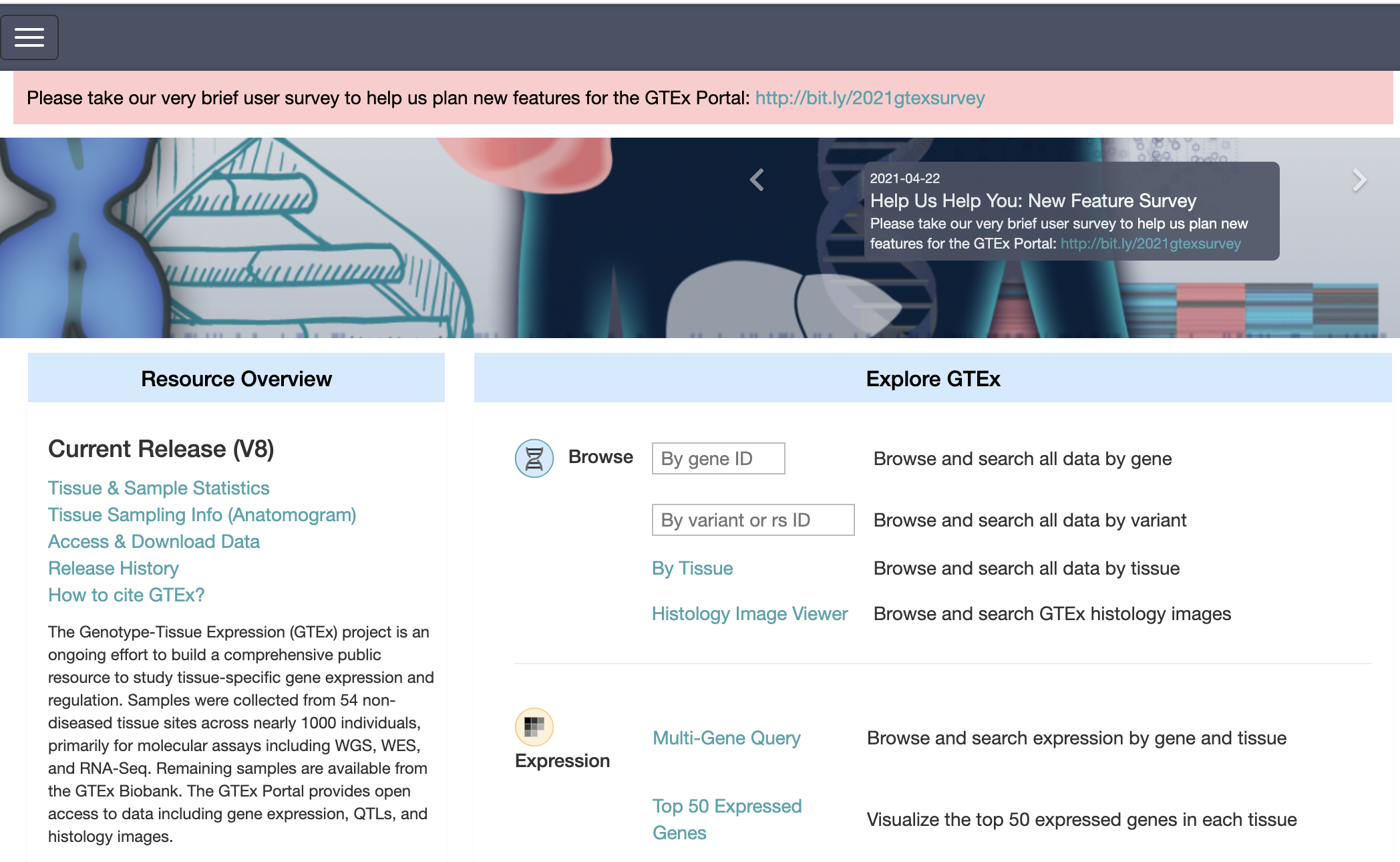
The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) Portal provides open access to data including gene expression, QTLs, and histology static.
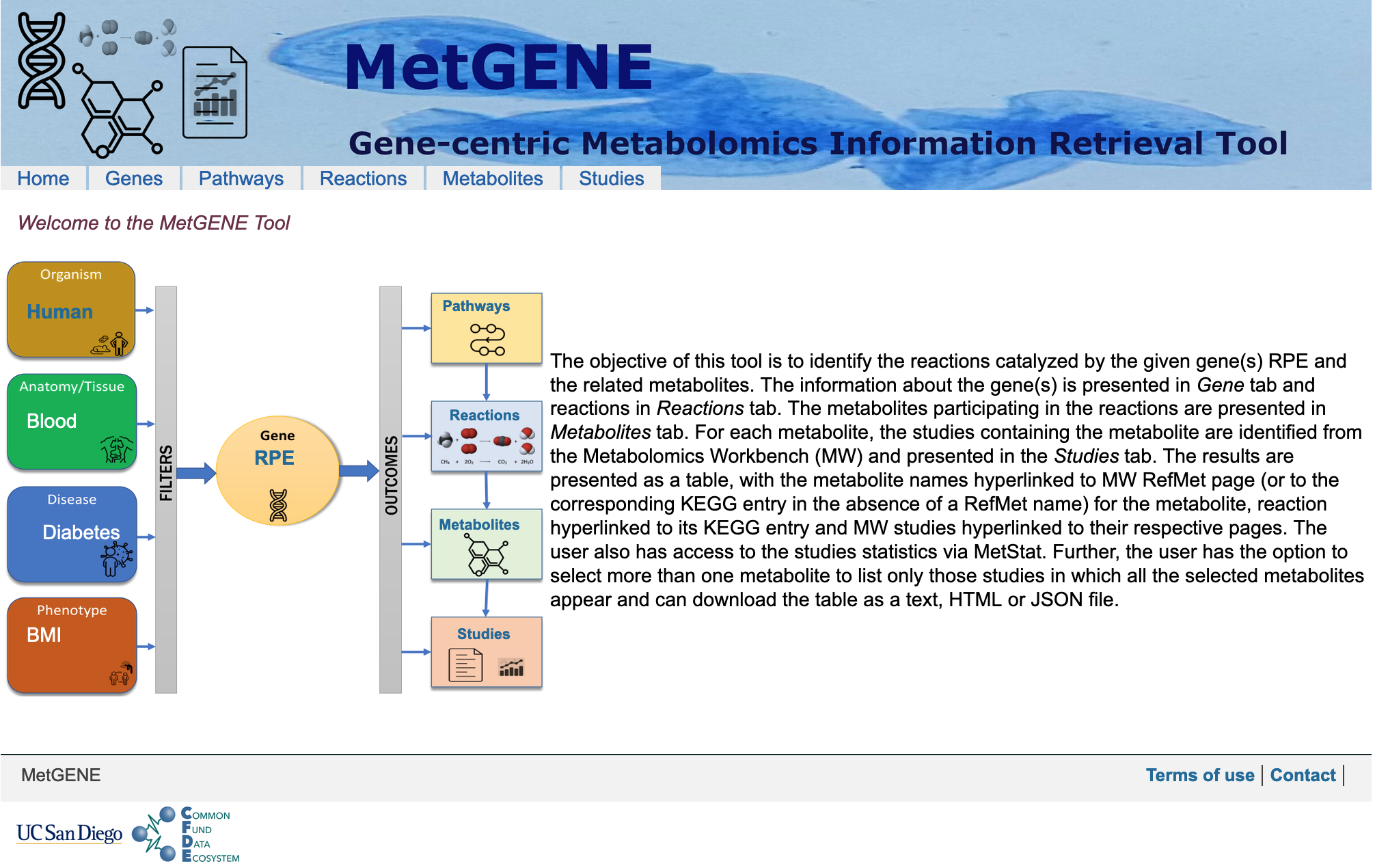
The objective of MetGENE is to identify the reactions catalyzed by the given gene(s) RPE and the related metabolites.
Reactome is a free, open-source, curated and peer-reviewed pathway database that provides intuitive bioinformatics tools for the visualization, interpretation and analysis of pathway knowledge.
The RGCSRS Appyter provides visualizations of the RNA-seq signatures induced by CRISPR knockouts and chemical perturbagens. Signatures are computed from transformed data profiles from the LINCS L1000 data.
IDG Reactome Portal provides biologist-friendly way to visualize proteins, complexes, and reactions in high-quality Reactome pathways.
COSMIC, the Catalogue Of Somatic Mutations In Cancer, is the world's largest and most comprehensive resource for exploring the impact of somatic mutations in human cancer.
MARRVEL enables users to search multiple public variant databases simultaneously and provides a unified interface to facilitate the search process.
The Pharos interface provides facile access to most data types collected by the Knowledge Management Center for the IDG program.
The Monarch Initiative is an integrative data and analytic platform connecting phenotypes to genotypes across species, bridging basic and applied research with semantics-based analysis.
Gene Centric GEO Reverse Search Appyter enables users to query for a gene in a species of interest; it returns an interactive volcano plot of signatures in which the gene is up- or down-regulated.
The Knockout Mouse Programme - International Mouse Phenotyping Consortium (KOMP-IMPC) has information about the functions of protein-coding genes in the mouse genome.
Bgee is a database for retrieval and comparison of gene expression patterns across multiple animal species.
BioGPS is a free extensible and customizable gene annotation portal, a complete resource for learning about gene and protein function.
KEGG is a database resource for understanding high-level functions and utilities of the biological system from molecular-level information.
WikiPathways was established to facilitate the contribution and maintenance of pathway information by the biology community.
The HGNC database is a curated online repository of approved gene nomenclature, gene groups and associated resources including links to genomic, proteomic and phenotypic information.
The NCBI Gene Database page provides information about nomenclature, RefSeqs, maps, pathways, variations, phenotypes, and links to genome-, phenotype-, and locus-specific resources.
PDB has information about the 3D shapes of proteins, nucleic acids, and complex assemblies that contribute to understanding everything from protein synthesis to health and disease.

PubMed comprises more than 33 million citations for biomedical literature from MEDLINE, life science journals, and online books.
Ensembl is a genome browser for vertebrate genomes that supports research in comparative genomics, evolution, sequence variation and transcriptional regulation.